
Contact information
christian.siebold@strubi.ox.ac.uk
Professor Christian Siebold Research Group
Henry Wellcome Building of Genomic Medicine
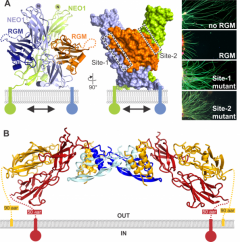 |
(A) Repulsive Guidance Molecule (RGM) in complex with its receptor NEO1 (Science 2013, Cell 2021). (B) RGM-NEO1-BMP complex, revealing that RGM bridges the NEO1 and BMP morphogen pathways (Nature Struct Mol Biol 2015). |
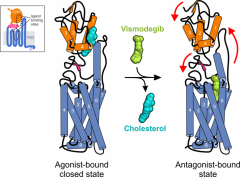 |
| Structures of the GPCR and oncoprotein Smoothened bound its agonist cholesterol and the cancer drug vismodegib (Nature 2016, ELife 2016, Nature Chem Biol 2019 and 2020, Science Adv 2022). |
Christian Siebold
Professor of Structural Biology
Structural studies on Morphogen Signalling
Only a handful of secreted morphogen signalling molecules, acting in a spatial and gradient-dependent manner, orchestrate the development of multicellular organism. Morphogen dysfunction leads to a range of diseases and defects in adult stem cell populations. Their importance in human disease has become increasingly clear over the past decade: dysfunctions of the pathways o lead to severe developmental and neurological diseases, and cancer.
Our group seeks to generate mechanistic insights relevant to disease and embryonic development focusing on two fundamental morphogen signalling systems: the functionally-intertwined Hedgehog (HH) and the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathways. Abnormal HH and BMP signalling often confers oncogenic properties to cells including uncontrolled proliferation, apoptosis inhibition, metastatic migration and cancer stem cell self-renewal. Hence, blocking excessive morphogen signalling provides a unique mechanism-based anti-tumour strategy. Our objective is to provide molecular insights into the extracellular initiation, modulation and transduction of HH and BMP signals to understand fundamental biological principles and disease mechanisms, and how these can be used for therapeutic approaches.
To achieve this, we are using structural biology techniques such as cryo electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography to obtain molecular snapshots of HH and BMP interactions with other proteins. We combine atomic details from structural and biophysical studies on single molecules with analyses of HH and BMP function in living cells. To test our hypotheses, we work together with developmental, cellular and cancer biologists, as well as chemists to provide an integrative understanding of these pathways and explore translational opportunities, for example in cancer therapy.
Key publications
-
Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of Hedgehog acyltransferase
Journal article
Coupland CE. et al, (2021), Molecular Cell, 81, 5025 - 5038.e10
-
Simultaneous binding of Guidance Cues NET1 and RGM blocks extracellular NEO1 signaling.
Journal article
Robinson RA. et al, (2021), Cell, 184, 2103 - 2120.e31
-
The morphogen Sonic hedgehog inhibits its receptor Patched by a pincer grasp mechanism.
Journal article
Rudolf AF. et al, (2019), Nature chemical biology, 15, 975 - 982
-
Structural basis of Smoothened regulation by its extracellular domains
Journal article
Byrne EFX. et al, (2016), Nature, 535, 517 - 522
-
Structure of the Repulsive Guidance Molecule (RGM)–Neogenin Signaling Hub
Journal article
Bell CH. et al, (2013), Science, 341, 77 - 80
Recent publications
-
Docking for Smoothened antagonist chemotypes not susceptible to a vismodegib-resistance mutation.
Journal article
Titulaer WHC. et al, (2025), Eur J Med Chem, 296
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MGRN1 targets melanocortin receptors MC1R and MC4R via interactions with transmembrane adapters.
Journal article
Parashara P. et al, (2025), bioRxiv
-
Structure and function of the ROR2 cysteine-rich domain in vertebrate noncanonical WNT5A signaling.
Journal article
Griffiths SC. et al, (2024), eLife, 13
-
Mapping structural and dynamic divergence across the MBOAT family.
Journal article
Ansell TB. et al, (2024), Structure (London, England : 1993)

